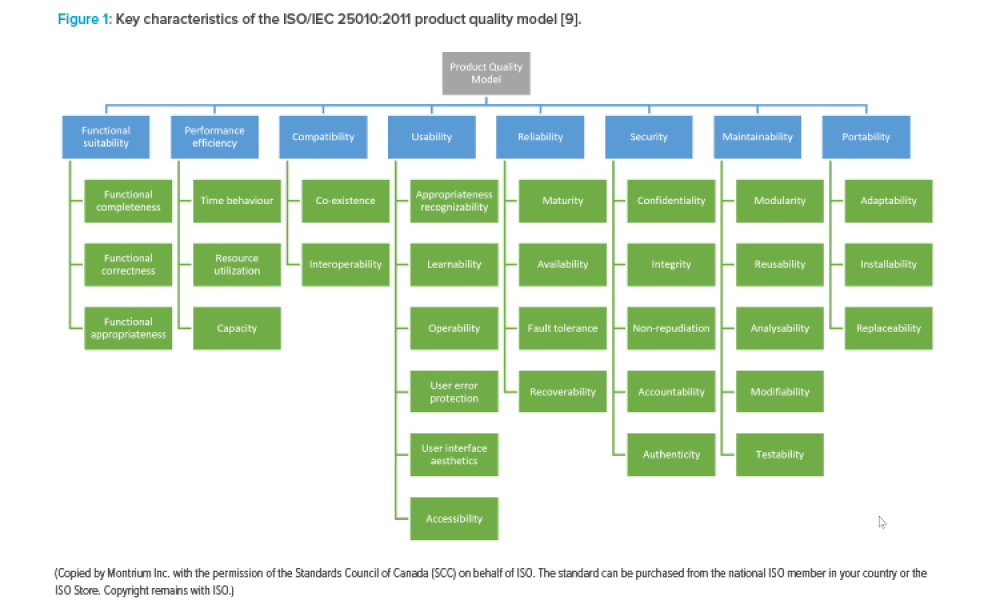
This article aims to refresh information on open-source software (OSS) within regulated computerized systems that was first discussed in an article in May-June 2010 Pharmaceutical Engineering®. The adoption of OSS advanced since then, and the article explores the importance of recognizing when an organization is relying on OSS and the benefits and risks this brings from a GAMP® 5...

Downloads
GAMP® Considerations When Relying on Open-Source Software
Cover: This article aims to refresh information on open-source software (OSS) within regulated computerized systems that was first discussed in an article in May-June 2010 Pharmaceutical Engineering®. The adoption of OSS advanced since then, and the article explores the importance of recognizing when an organization is relying on OSS and the benefits and risks this brings from a GAMP® 5 perspective.
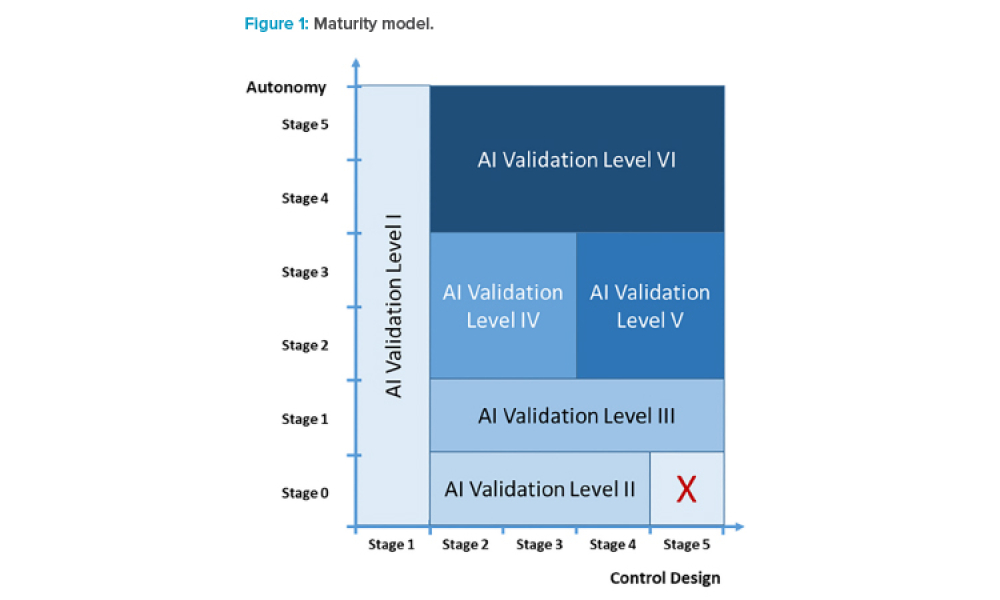
AI Maturity Model for GxP Application: A Foundation for AI Validation
Feature: Artificial intelligence (AI) has become one of the supporting pillars for digitalization in many areas of the business world. The pharmaceutical industry and its GxP-regulated areas also want to use AI in a beneficial way. Several pharmaceutical companies are currently running digital pilots, but only a small fraction follows a systematic approach for the digitalization of their operations and validation. However, the assurance of integrity and quality of outputs via computerized system validation is essential for applications in GxP environments. If validation is not considered from the beginning, there is considerable risk for AI-based digital pilots to get stuck in the pilot phase and not move on to operations.
Quality Agreements for SAAS Solutions Intended for GxP Use
Feature:As adoption of cloud technology continues to increase across the life sciences industry, so too does the need to establish a standardized and pragmatic approach for ensuring the quality of software applications used in support of GxP data and associated processes. This article focuses on the application level and the growing use of software as a service (SaaS) within the life sciences industry.
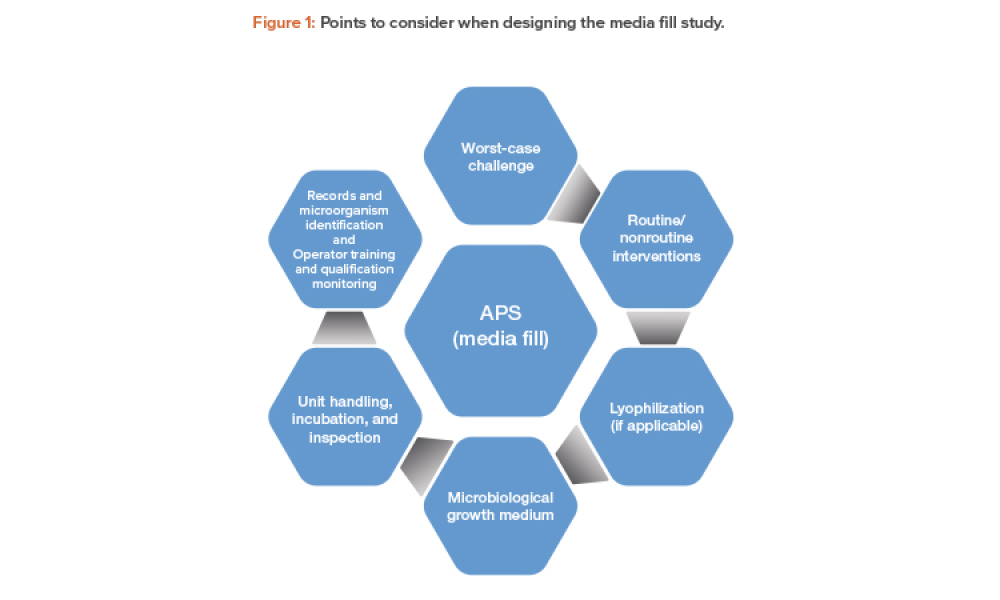
Validation of Aseptic Processes Using Media Fill
Technical: Aseptic process simulation (APS) is essential for validation of an aseptic manufacturing process and is required by regulators to demonstrate the aseptic capability of such processes. A successful program of APS and aseptic manufacturing requires significant operator training, skills, and supervision; thorough maintenance; effective cleaning and disinfection; significant oversight of every aspect of the operation by quality assurance; and microbiological monitoring by quality control.
Lessons Learned in Global CQV
Technical: Global commissioning, qualifi cation, and validation (CQV) project delivery has in recent years been required to push the boundaries on delivery methodologies and techniques to ensure sufficient production capacity is available to meet ever-expanding patient needs. This article focuses on lessons captured in the execution and resource management of large-scale global CQV projects in an environment of change and compressed project timelines
In This Issue
Pandemic or no pandemic, the pharmaceutical industry is growing at an unprecedented pace, and it is very gratifying to be part of that process. COVID-19 has brought our industry to the daily news, and while the public is getting a better grasp of how we work and need to work, there are still so many misconceptions that need clarification.
Now that the year is underway and people continue to learn how to live with COVID-19, there appear to be some areas where life and work will be changed for an extended period. Adapting and coming up with new tools and approaches will be key.
Eamon Judge, the 2020 recipient of the Max Seales Yonker Member of the Year award, exemplifies the values behind the award: service to the industry and inspiring ISPE members to volunteer.
The ISPE Annual Meeting & Expo is our signature event, uniting the pharmaceutical industry’s best and brightest to share their expertise, showcase their brands, and network. The 2021 ISPE Annual Meeting ...
Aseptic process simulation (APS) is essential for validation of an aseptic manufacturing process and is required by regulators to demonstrate the aseptic capability of such processes. A successful program of APS and aseptic manufacturing requires significant operator training, skills, and supervision; thorough maintenance; effective cleaning and disinfection; significant oversight of every...
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become one of the supporting pillars for digitalization in many areas of the business world. The pharmaceutical industry and its GxP-regulated areas also want to use AI in a beneficial way. Several pharmaceutical companies are currently running digital pilots, but only a small fraction follows a systematic approach for the
With the publication of recent guidance, specifically the US FDA Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical cGMP Regulations
Global commissioning, qualification, and validation (CQV) project delivery has in recent years been required to push the boundaries on delivery methodologies and techniques to ensure sufficient production capacity is available to meet ever-expanding patient needs. This article focuses on lessons captured in the execution and resource management of large-scale global CQV projects in an...
As adoption of cloud technology continues to increase across the life sciences industry, so too does the need to establish a standardized and pragmatic approach for ensuring the quality of software applications used in support of GxP data and associated processes. This article focuses on the application level and the growing use of software as a service (SaaS) within the life sciences...