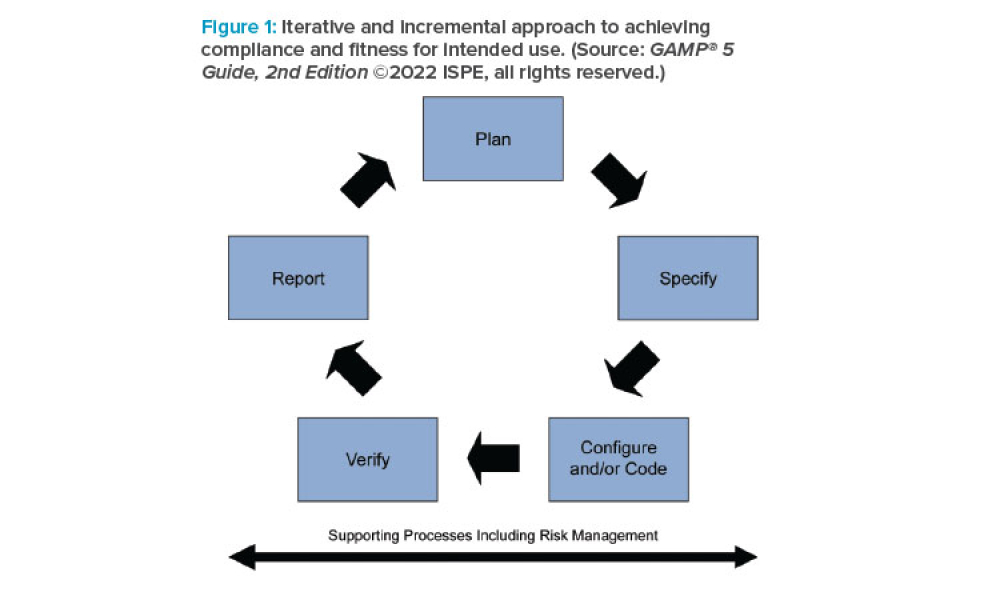
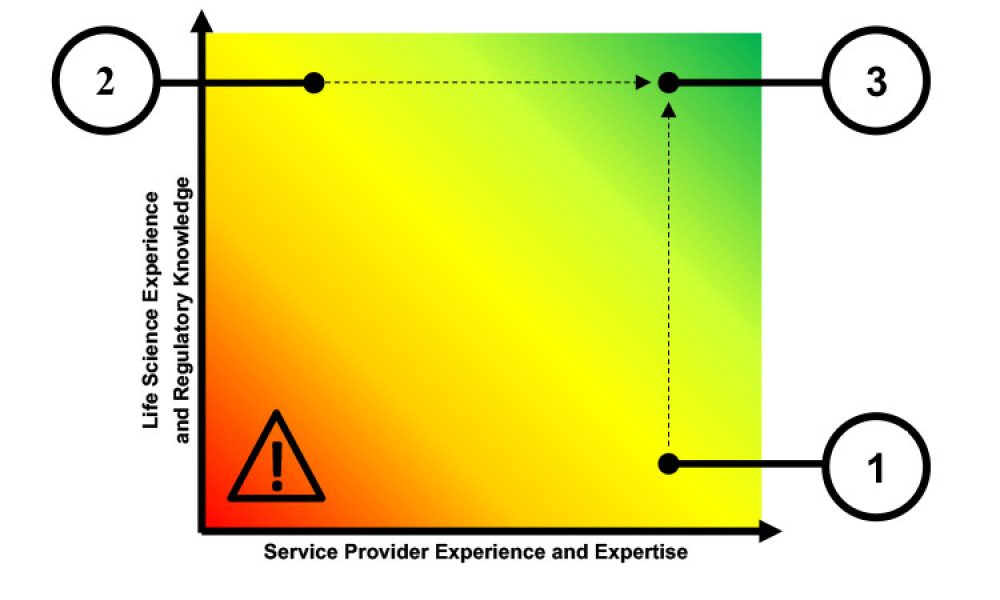
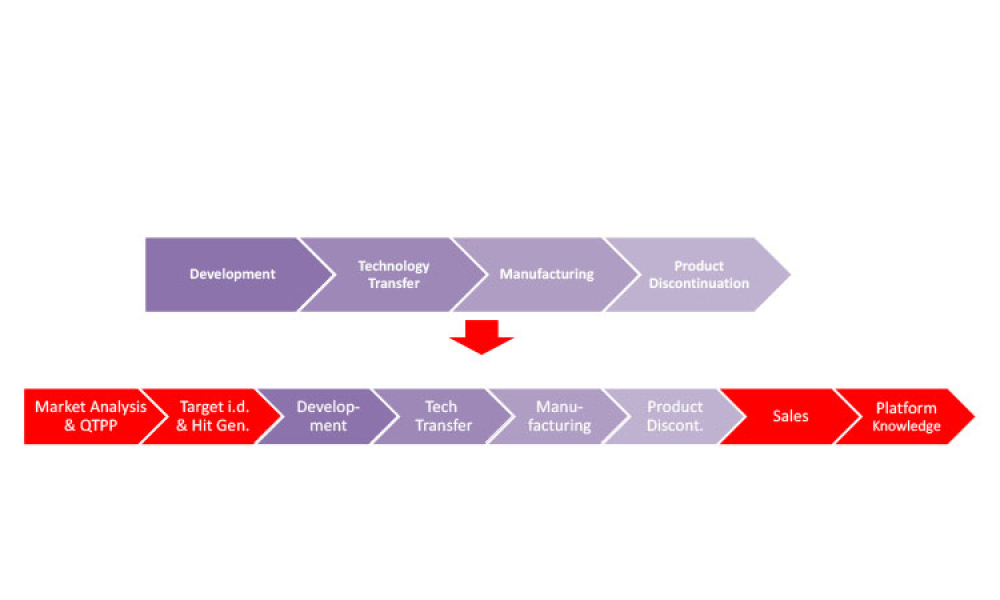
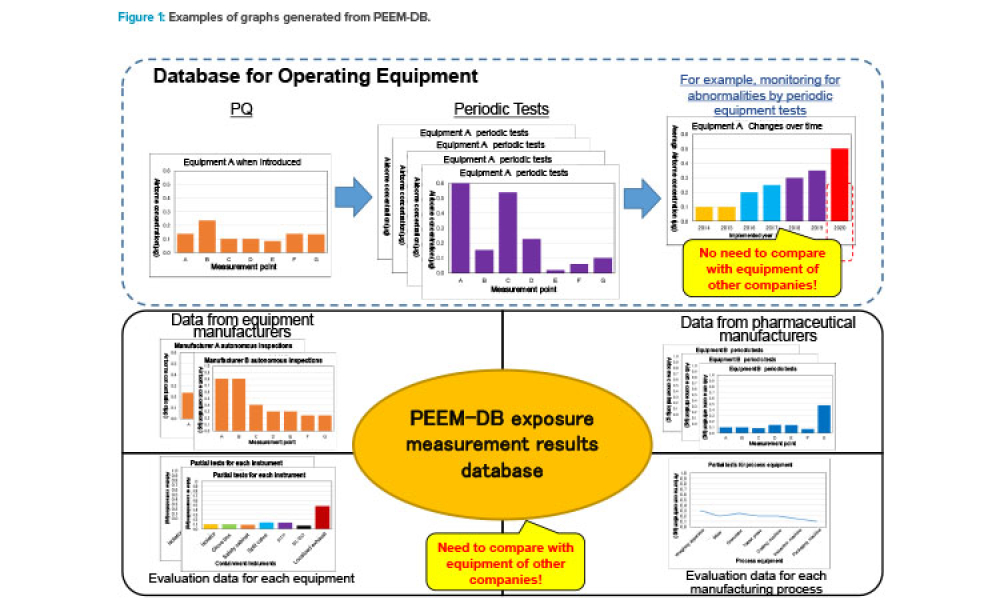
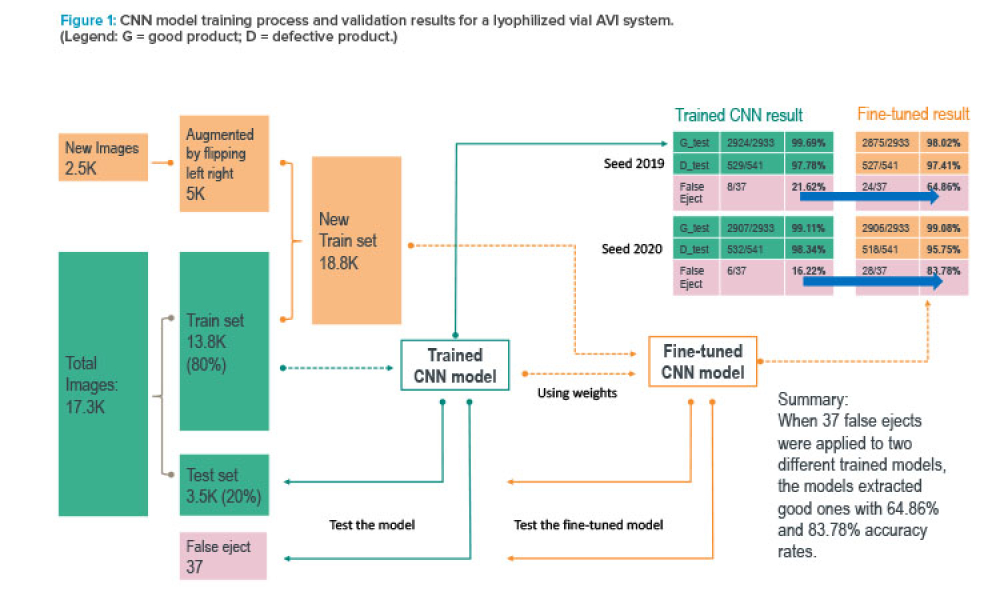
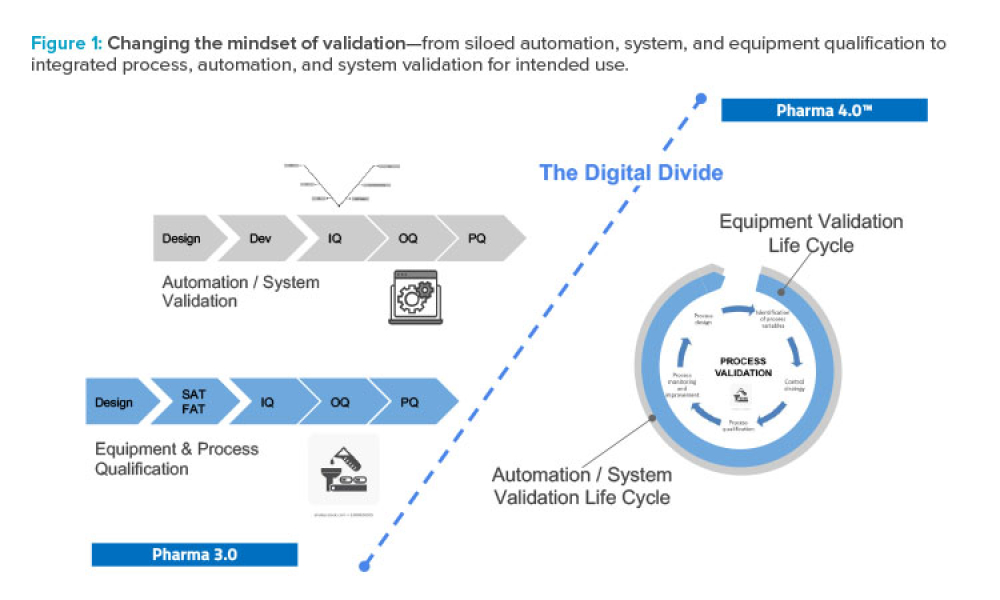
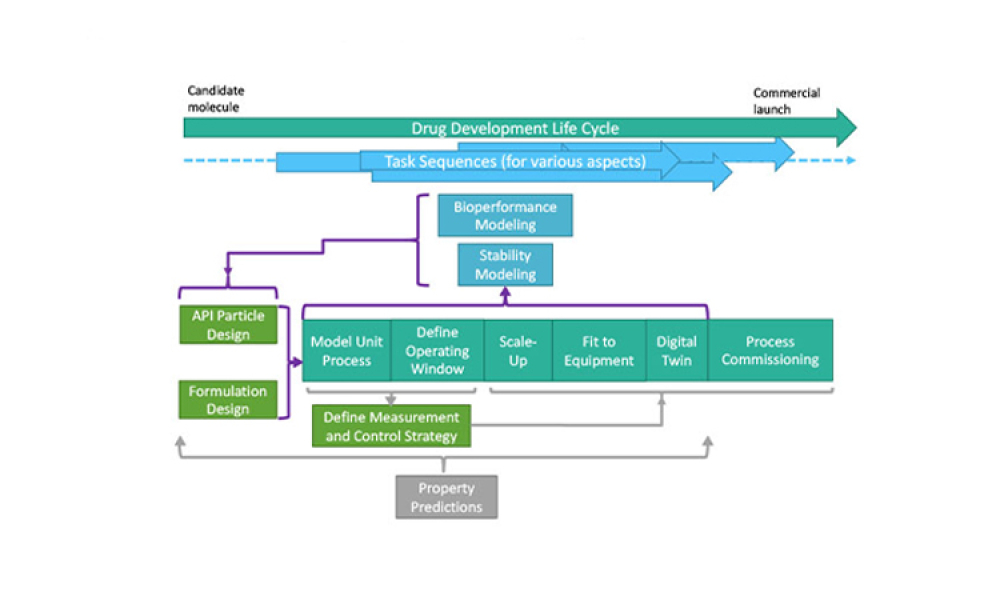
Computer software assurance (CSA) has been discussed widely in industry over the past five years. While the principles are well understood and welcomed, until now some of the practical detail on how exactly to implement CSA into an organization has been missing.
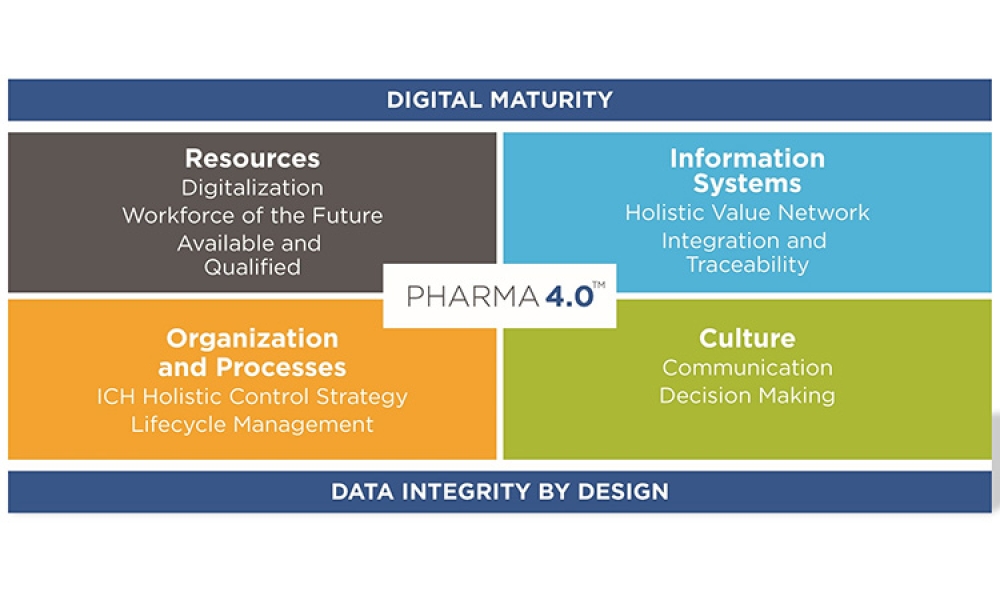
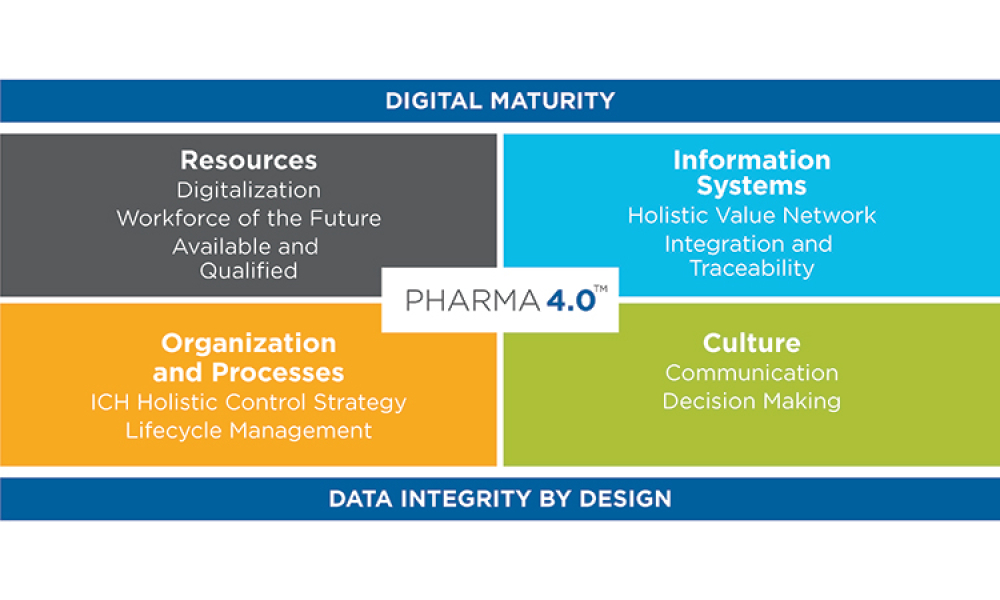
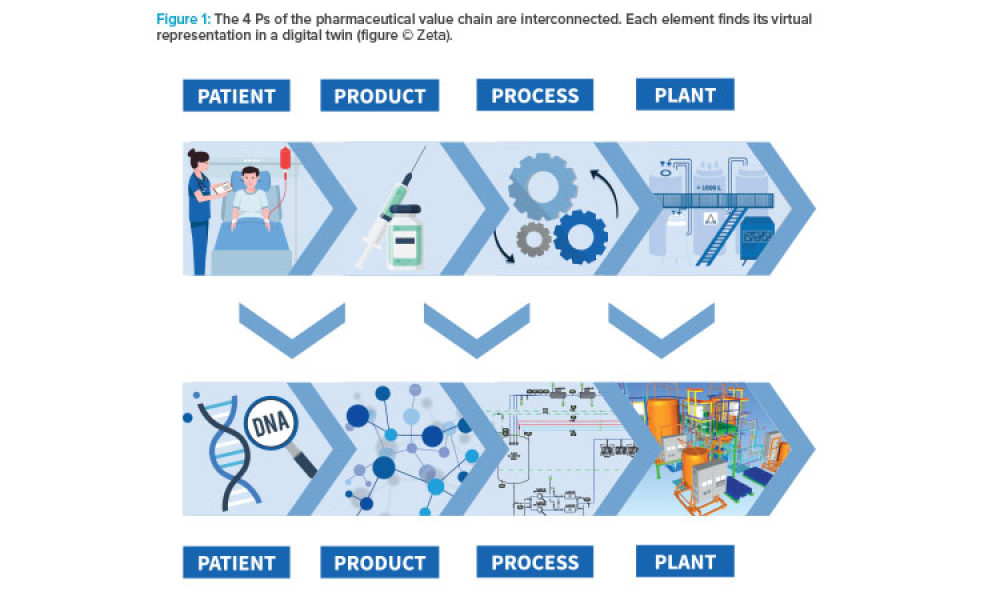
The pharmaceutical industry stands at the precipice of a revolution as emerging digital technologies provide new opportunities to boost productivity through continuous process improvements. The Pharma 4.0™ framework, an adaptation of the broader Industry 4.0 movement, aims to transform how drugs are produced and delivered.