ISPE held an Expert Xchange on 18 January 2022 entitled “Risk-Based Decision Making: Advancing the Integration of Quality Risk Management (QRM) and Knowledge Management (KM).” The session included presentations and interactive exercises that generated new and useful insights into the current effectiveness of the knowledge that flows into QRM and how a knowledge map can be used to diagnose...

Downloads
Integrating Knowledge Management and Quality Risk Management
Cover: ISPE held an Expert Xchange on 18 January 2022 that included presentations and interactive exercises that generated new and useful insights into the current effectiveness of the knowledge that flows into QRM and how a knowledge map can be used to diagnose opportunities to improve KM. The exercises also helped identify the types of knowledge generated during QRM. These insights demonstrated the opportunity to improve risk-based decision-making by uniting risk and knowledge through a suitable framework such as the Risk-Knowledge Infinity (RKI) Cycle.
From Data to Knowledge Management: What to Consider
Feature: Although data and knowledge are both stand-alone disciplines that need to be systematically managed, they also must have a connection. Understanding the relationship between data and knowledge management processes and how people are leveraging advances like Pharma 4.0™ combined with these processes enables quality data transition to knowledge that can help pharmaceutical companies. The authors also want to generate understanding on how using the knowledge acquired by people through experience (tacit knowledge) can further connect both data and knowledge management systems, yield positive strategic results, and deliver more efficient processes within organizations.
Effective Knowledge Management in Mergers and Acquisitions
Feature: As the pharmaceutical industry continues to grow and evolve, a significant contributor to innovation and evolution is mergers and acquisitions. In the pharmaceutical industry, knowledge management has been identified as an enabler to a pharmaceutical quality system through the publication of ICH Q10. This article discusses, at a high level, the potential opportunities of KM contributing to the success of pharmaceutical merger acquisitions through end-to-end knowledge transfer.
AI Governance and QA Framework: AI Governance Process Design
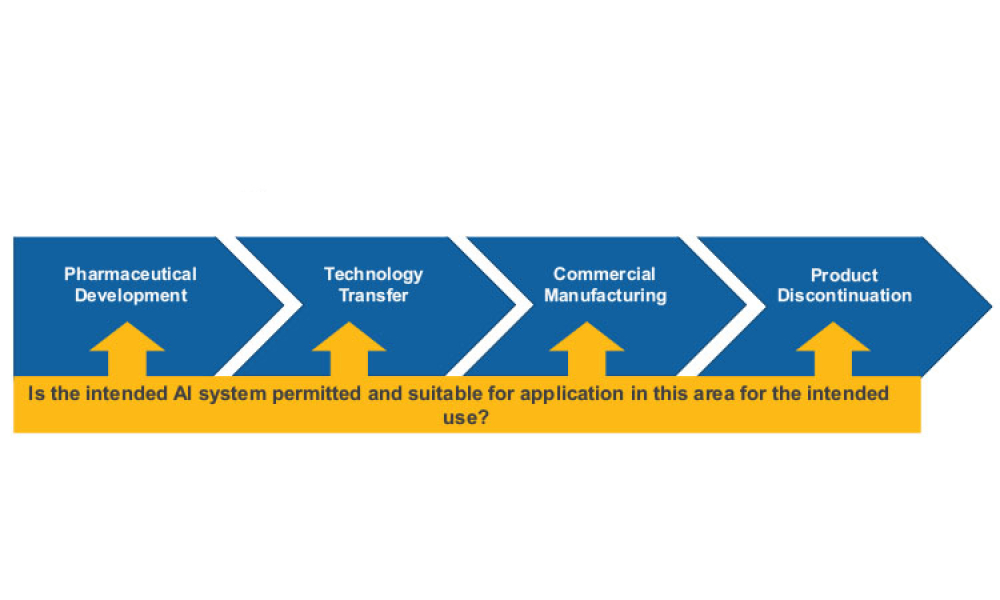
Technical: Artificial intelligence has the potential to benefit the pharmaceutical industry and its GxP-regulated areas. However, project implementation remains limited, mostly due to a lack of robust validation procedures. Hence, there is a need to develop a robust governance framework to ensure that integration of AI into workflows is possible while simultaneously ensuring that evaluation standards are still met. The proposed framework presented in this article provides a general organizational and procedural structure for developing and sustaining AI solutions in GxP-relevant contexts.
In This Issue
Why do I volunteer at ISPE? It is a question that I and surely many of you get asked. Indeed, why?
Knowledge management is powerful. It can be a catalyst for organizational success and create a major competitive advantage, or be a major contributor to organizational failure. We live in a world today where knowledge is literally at our fingertips. To access knowledge in quite literally any topic, we Google it. Merriam-Webster has even added the word “google” as a verb to the dictionary.
When opportunity presents itself, how do we know? And who is the opportunity for? How do we evaluate and determine if it is a “good” opportunity? What needs to line up in order to point all the arrows to “yes”?
ISPE has more than 17 global Communities of Practice (CoPs) where members can connect with each other. Professional Communities of Practices for
Effective and timely management of change throughout the product life cycle enables quality improvement and is critical to patient safety, supply reliability, and operational effectiveness and efficiency. The ISPE Advancing Pharmaceutical Quality (APQ) Guide: Change Management System provides a quality management framework for assessing and advancing change management (CM) system maturity...
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to benefit the pharmaceutical industry and its GxP-regulated areas. Several pharmaceutical companies are currently running digital pilots; 90% of large pharmaceutical companies have initiated AI projects.1
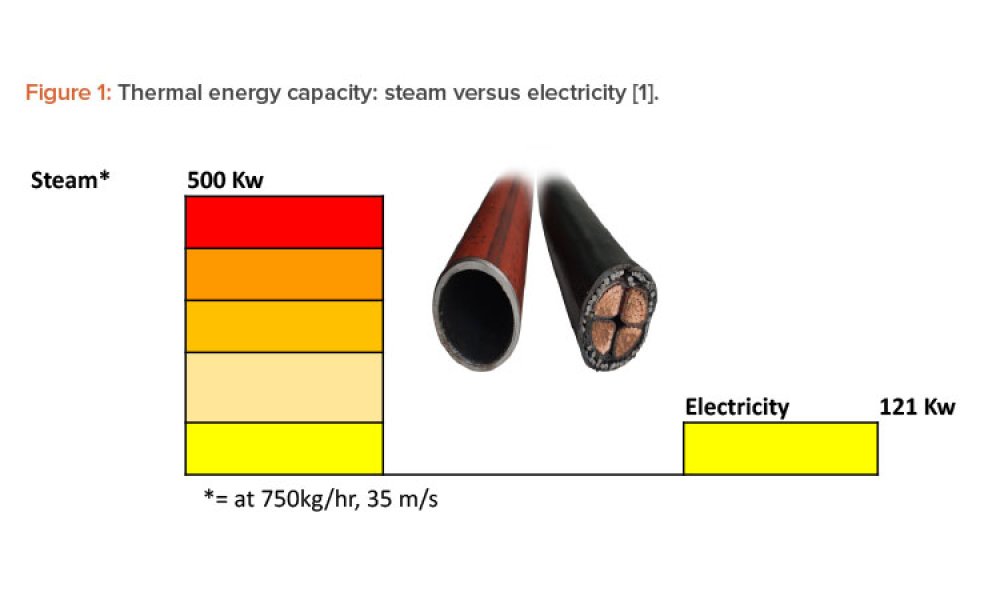
Steam is the most powerful and effective thermal energy transfer fluid, and its use continues to grow in process industries around the world. However, there is very little written about the commissioning and qualification of pharmaceutical pure steam systems in GMP regulations or regulatory guidance. This article provides the background and science behind the steam quality tests and proposes a...
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to grow and evolve, a significant contributor to innovation and evolution is mergers and acquisitions (M&A). M&A can enable academic researchers and small companies to fund and commercialize innovative products. In addition, M&A can help larger organizations secure new and complementary technology and products. In the pharmaceutical...
As the industry experiences significant changes to the way we do business, knowledge capture and sharing are more important now than ever before. The maturing digitalization of the biopharma industry’s business and processes is creating an increasingly data- and information-rich environment that requires more effective mechanisms for sharing data and information. The Knowledge Management team...
On 26 January 2022, representatives of the author team for the ISPE Good Practice Guide: Knowledge Management in the Pharmaceutical Industry held a webinar to provide an...
Although data and knowledge are both stand-alone disciplines that need to be systematically managed, they also must have a connection. Understanding the relationship between data and knowledge management processes and how people are leveraging advances like Pharma 4.0™ combined with these processes enables quality data transition to knowledge that can help pharmaceutical companies. The authors...