- Green synthesis: Pharmaceutical laboratories can develop new and greener synthetic routes for drug production. This includes the utilization of renewable feedstocks, development of environmentally friendly synthetic methodologies, and the use of biocatalysts or enzymes.
- Analytical techniques: Green chemistry promotes the use of analytical techniques that minimize or eliminate the use of hazardous reagents. Pharmaceutical laboratories can implement techniques such as green chromatography, spectroscopy, or bioassays to reduce their environmental impact.
- Continuous flow synthesis: Continuous flow synthesis is a technique that enables the production of pharmaceuticals on a continuous basis, allowing for better control and optimization of reactions. Continuous flow systems can enhance atom economy by reducing the amount of unused starting materials and minimizing waste generation.
- Synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs): Traditional synthetic methods often involve the use of toxic solvents, heavy metals, and hazardous reagents, which pose health risks to laboratory personnel and have a detrimental impact on the environment. Green chemistry approaches seek to replace these harmful chemicals with greener alternatives and develop more efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis routes.
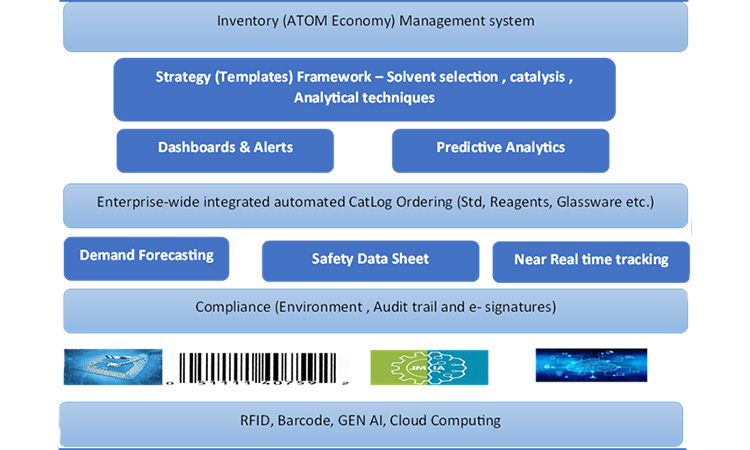
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Green Chemistry
Generative AI (gen AI) has the potential to revolutionize green chemistry in pharmaceutical laboratories. By utilizing AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, researchers can optimize chemical reactions and predict the best conditions for maximum yield and minimal waste. This not only saves time and resources but also reduces the number of experiments required, leading to a more sustainable and cost-effective drug development process.
Gen AI can also aid in the discovery of novel green solvents and catalysts. Traditional solvents used in pharmaceutical laboratories, such as chloroform and dichloromethane, are known to be hazardous and contribute to air pollution and water contamination. Gen AI can analyze vast amounts of data and identify alternative solvents that are less toxic, biodegradable, and renewable, thereby minimizing their environmental impact.
Furthermore, gen AI can assist in the design of pharmaceutical compounds with improved biodegradability and reduced toxicity. By analyzing the molecular structure and properties of existing drugs, AI algorithms can propose modifications that enhance their environmental profile while maintaining desired therapeutic activity. This approach aligns with the principles of green chemistry, which prioritize the development of sustainable and eco-friendly pharmaceuticals.
In conclusion, the integration of gen AI and green chemistry in pharmaceutical laboratories holds significant promise for advancing sustainable drug discovery and development. By optimizing chemical processes, identifying greener solvents and catalysts, and designing environmentally friendly compounds, researchers can minimize the environmental impact of the pharmaceutical industry and contribute towards a more sustainable future., ,
Disclaimer:
iSpeak Blog posts provide an opportunity for the dissemination of ideas and opinions on topics impacting the pharmaceutical industry. Ideas and opinions expressed in iSpeak Blog posts are those of the author(s) and publication thereof does not imply endorsement by ISPE.