SPuMoNI: Enhancing Pharma Data Quality through Smart Technologies

Funded by the European Commission from 2019, the Smart Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Project (SPuMoNI)1 harnesses the potential of state-of-the-art technologies for the pharmaceutical industry. This article discusses the main SPuMoNI accomplishments.
The Falsified Medicines Directive “introduces harmonised European measures to fight medicine falsifications and ensure that medicines are safe and that the trade in medicines is rigorously controlled.”2 Such obligatory safety features, legal framework, and record-keeping requirements have arguably imposed stricter controls for manufacturing of medicaments.
Although the pharmaceutical industry has consistently improved manufacturing processes3 in compliance with good manufacturing practices,4 there are documented deviations from good practices5 including the continued falsification of medicines.6 (Note: The terms “pharmaceutical” and “pharma” interchangeably employ throughout this article.) Disclosure risk assessment techniques in pharma manufacturing typically depend on background knowledge, the behavior of intruders, and the specific value of the data. Often, only heuristic arguments are used, without numerical assessment.7
The SPuMoNI consortium comprises two pharma industrial partners—PQE Group and FAREVA’s Instituto De Angeli—and three academic institutions: the Universitat Politècnica de València (Spain), the University of Thessaly (Greece), and the National College of Ireland (Ireland). SPuMoNI utilizes state-of-the-art technologies to support a smarter industry. These technologies include blockchain for end-to-end verification of manufacturing data, quality assurance methods for data integrity compliance, and modern artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to smartly extract, transform, and control heterogeneous data sources within the manufacturing processes to better improve big-data quality and process modeling for a smarter industry.8
SPuMoNI leverages blockchain technologies to better ascribe and ensure the manufacturing traceability of medicaments. SPuMoNI is particularly timely because blockchain has been proposed to become “a new digital service infrastructure” for Europe.9 Although blockchain is well-established in the cryptocurrency domain, the systematic application of smart contracts in the pharma industry remains an open problem.10, 11 Moreover, traceability in manufacturing12 has traditionally been studied in the food industry, but rarely in pharmaceutical manufacturing, consequently attracting some industry attention.13
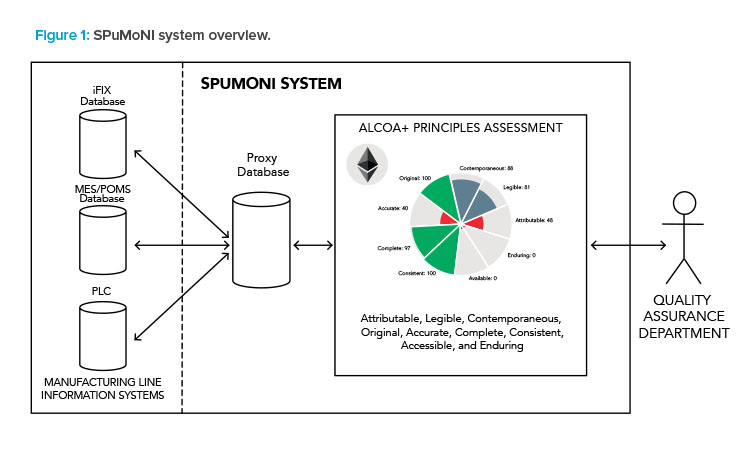
In this respect, ensuring data integrity in compliance with the current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) regulations by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) means ensuring quality assessment of batch reports, audit trails, and system registries in terms of the ALCOA+ principles: attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, accurate, complete, consistent, accessible, and enduring.
SPuMoNI has produced an innovative scientific approach to systematically establish and ensure constant proof of the authenticity of pharmaceutical manufacturing data and to develop a user-friendly software tool for pharmaceutical officers, following the ISPE GAMP© validation standards, during both the IT development and the use of a qualified IT infrastructure.
End-to-End Verification
Blockchains and smart contracts implement peer-to-peer networks formed by “blocks,” creating a distributed ledger where data from one block can only be altered by modifying all subsequent blocks. In the SPuMoNI system, data are stored within a blockchain as tamper-proof data transactions, ensuring that SPuMoNI datasets remain unaltered with a measurable quality of service.8 Following General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and pharmaceutical industry regulations, SPuMoNI uses its own private Ethereum blockchain network, hosted at National College of Ireland’s OpenStack private cloud, to store data descriptors that should remain confidential with a guaranteed data integrity.
Data Quality Assurance
Data quality assurance targets ALCOA+ compliance, including single- and multiple-batch evaluation analysis by data quality metrics. The single-batch evaluation checks each ALCOA+ principle of the corresponding batch, and the multiple-batch evaluation includes a temporal and multisource variability characterization of both the ALCOA+ principles and specific variables of manufacturing sensors.
SPuMoNI Today
Currently running in its latest stages and with a proof of concept already available upon request for demonstration, the SPuMoNI system delivers an AL-COA+ assessment to ensure continuous data integrity of pharma manufacturing reports (see Figure 1).14
Furthermore, SPuMoNI has achieved the following significant results in the past three years:
- Collected anonymized datasets with discrete and specific attributes related to environmental conditions of different pharma systems, which are useful for the development of software that already structures data in this fashion
- Issued data integrity guidelines to set the rules on how AI should process data and identify patterns that may lead to compliance issues
- Developed the base AI architecture and further developed additional AI applications for other manufacturing processes related to the pharmaceutical industry to assess data integrity compliance before validation/deployment
- Enhanced multi-node private blockchain networks to ensure data provenance and compliance in a tamper-proof manner
- Released SPuMoNI guidelines as a template of integrated software/network infrastructure for pharma manufacturing
- Deployed a prototype in an industrially relevant environment
As stated, SPuMoNI has produced an innovative scientific approach to systematically establish and ensure constant proof of the authenticity of pharmaceutical manufacturing data. Supported by an ALCOA+ assessment, the SPuMoNI system helps deliver enhanced data quality for the pharma industry.






