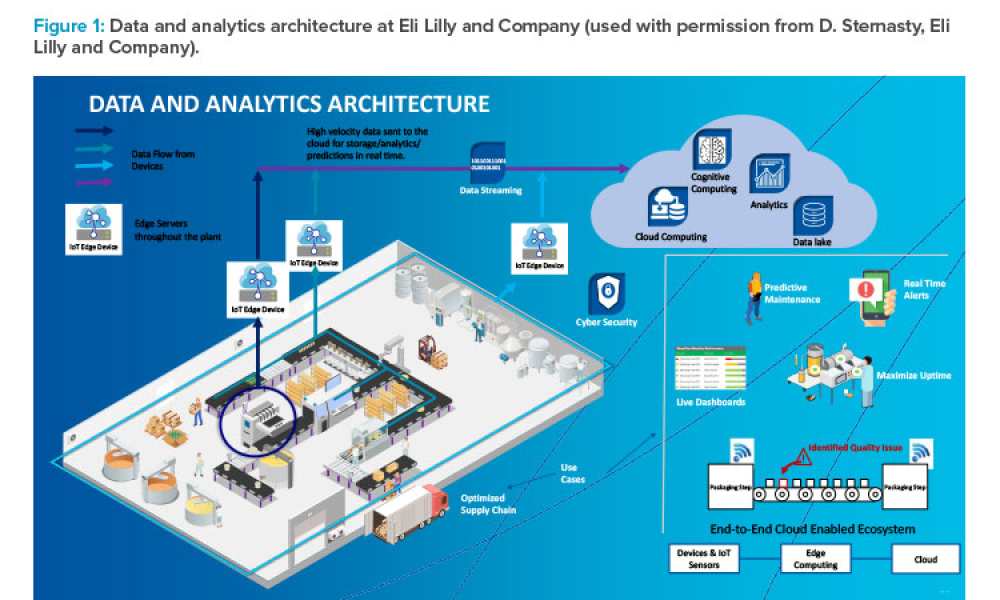
The ISPE Pharma 4.0™ Special Interest Group (SIG) launched in 2015 to provide a road map for new challenges of digitalization, Industry 4.0, and the smart factory. The Special Interest Group addresses how pharmaceutical industry stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, can achieve benefits from

Downloads
ISPE Pharma 4.0™ SIG & Its Working Groups
Cover: The ISPE Pharma 4.0™ Special Interest Group (SIG) launched in 2015 to provide a road map for new challenges of digitalization, Industry 4.0, and the smart factory. The SIG addresses how pharmaceutical industry stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, can achieve benefits from Pharma 4.0™ initiatives.
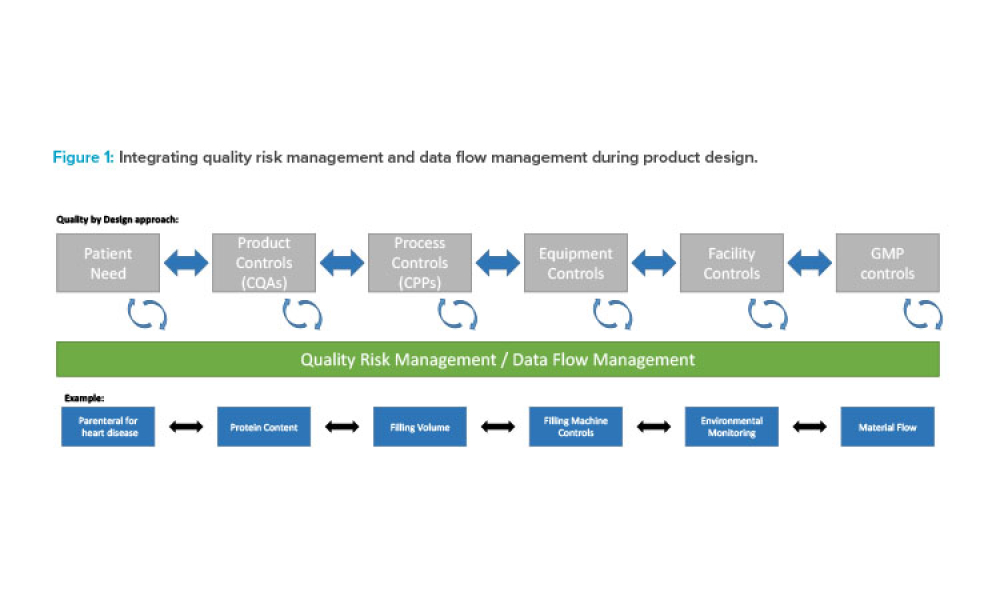
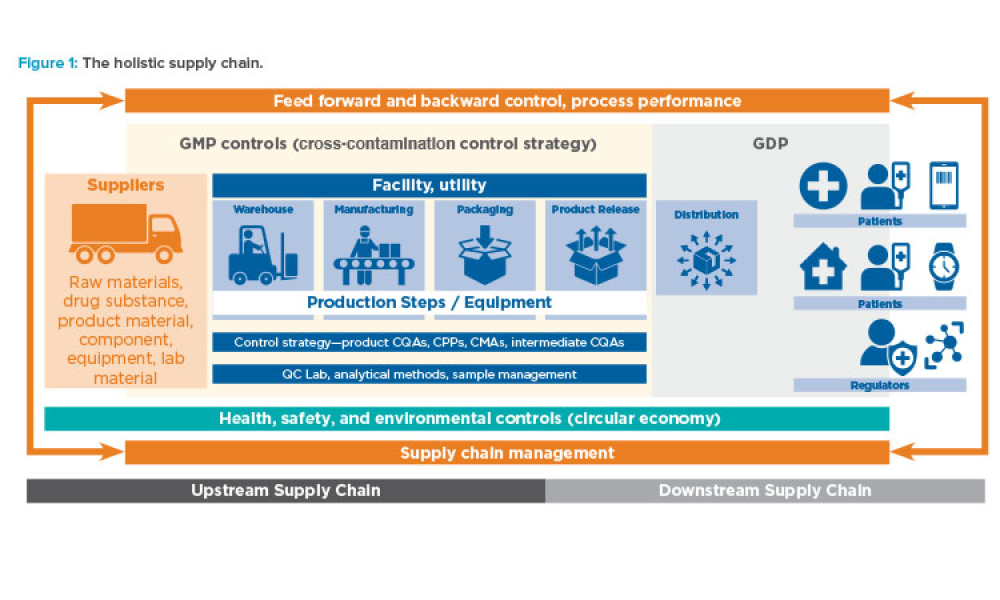
Holistic Control Strategy: From ICH Quality Guidelines to Pharma 4.0™
Feature: To ensure future success in the delivery of therapeutic medicines to patients, it is imperative that the pharmaceutical industry move deeper into the fourth Industrial Revolution and embrace increasingly advanced levels of digital maturity through Pharma 4.0™. This article discusses how holistic control strategy can be a bridge from established industry guidelines (ICH Q8–Q12) to the Pharma 4.0™ operating model.
Data Science for Pharma 4.0™, Drug Development, & Production—Part 1
Feature:The article hypothesizes that data science–derived manufacturing process and product understanding is the main driver of digitalization in the bioprocessing industry for biologics manufacturing. In this article, the first of a two-part series, the authors analyze the prerequisites for establishing data science solutions and present key data science tools relevant to the process development stage.
Breaking with Tradition: Laying the Foundation for Validation 4.0
Feature: If Industry 4.0 is to succeed in the pharma space as Pharma 4.0™, we need new paradigms for validation across the value chain that use new technologies to improve product quality and the safety of medicines and treatments for the patient. This article lays the foundation for shifting our mindset and achieving Validation 4.0.
Cleaning Validation
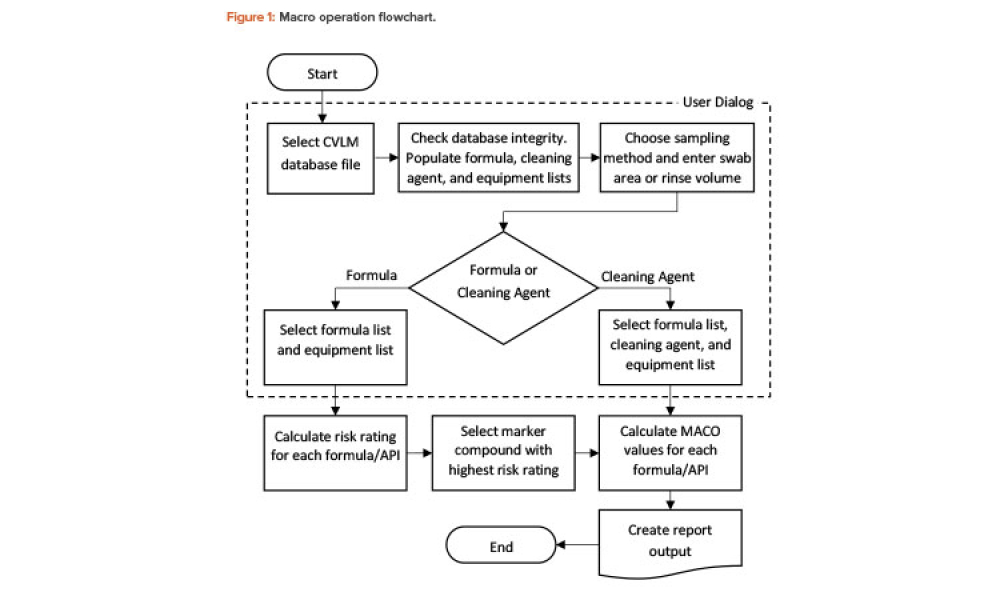
Technical: Automating MACO Calculations in Cleaning Validation For a multiproduct facility where equipment is shared, there is always risk from cross-contamination. The correct calculation of the cleaning validation limits from maximum allowable carryover (MACO) of a marker compound to the next product is vital for the integrity and success of the cleaning validation program. However, the process yielding those limits often involves cumbersome, error-prone manual calculations. The article describes an innovative yet simple tool that uses a combination of spreadsheet software and a statistical platform to fully automate science- and risk-based MACO calculations in pharmaceutical cleaning validation.
In This Issue
The last 12 months have felt like the slowest and fastest of times. The days drone on, yet the months fly by. I have now been working from home for a year—5% of my time at Lilly. I feel sadness for so many families who have lost loved ones and/or spent the holidays alone. Dogs and cats appearing in virtual meetings are no longer a huge distraction but a welcome glimpse of social...
Understanding and utilization of Pharma 4.0™ technologies will be critical for students and Emerging Leaders (ELs) as they develop in their careers in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. To learn more, I spoke with Edoardo Schiraldi, an Emerging Leader based in Florence, Italy, who works as a Corporate R&D Business Solutions Specialist with Menarini Group, about the “pillars”...
The ISPE Women in Pharma® (WIP) theme for the month of March is entrepreneurship. This word can mean different things to different people, but WIP defines it as the creation of value. Communications, events, and activities...
Through this difficult time of the COVID-19 pandemic, ISPE has remained active. At the 2020 ISPE Pharma 4.0™ Virtual Conference, 17–18 November, 174 attendees gathered online to discuss and learn about...
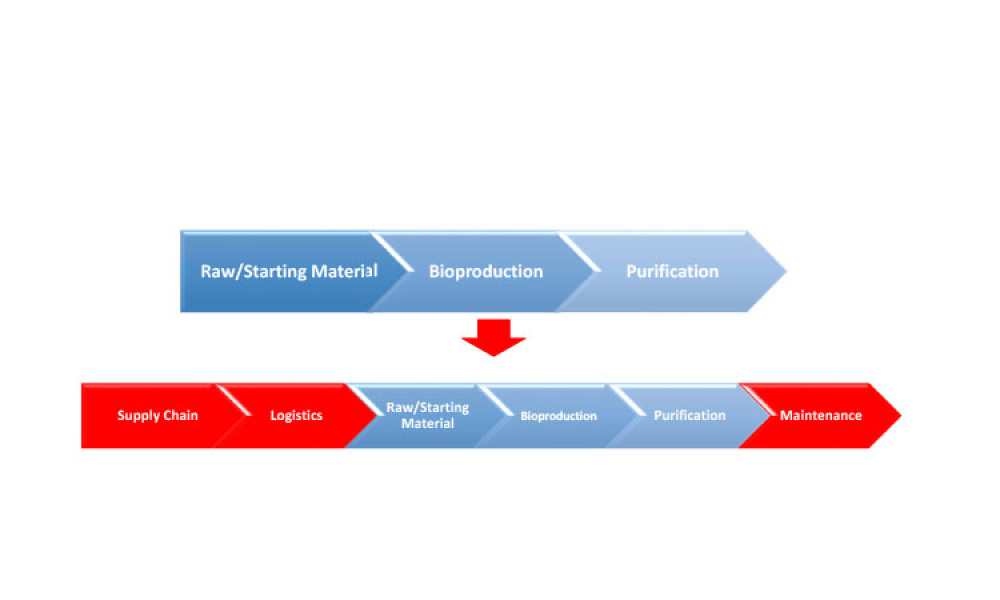
Equipment reliability helps reduce and manage the risk of failures in equipment, providing focus on availability, fitness for purpose, and cost. Reliable equipment improves the likelihood of achieving reliable manufacturing operations, which improves the supply of critical therapies to patients worldwide.
Digital transformation and digitalization are on the agenda for all organizations in the biopharmaceutical industry. But what are the main enablers of intelligent manufacturing? We hypothesize that data science–derived manufacturing process and product understanding is the main driver of digitalization in the bioprocessing industry for biologics manufacturing. In this article, the first of a...
Across every industry today, digitalization is driving the use and value of data to disrupt traditional business models and ways of working. In pharmaceuticals, the promises of Industry 4.0 are expected, and needed, to finally modernize the legacy approaches that have evolved since the 1970s. Validation is an obvious target for digital disruption because of the inefficient, document-heavy...
The ISPE Aseptic Conference will celebrate its 30th year with the virtual conference on 15–17 March. The conference has been setting the pace for the evolution of sterile manufacturing processes and technologies in...
The fourth Industrial Revolution (also known as Industry 4.0) is the era of smart machines, storage systems, and production plants that can autonomously exchange information, trigger actions, and control operations free of any human intervention. To ensure future success in the delivery of therapeutic medicines to patients, it is imperative that the pharmaceutical industry move deeper into the...
For a multiproduct facility where equipment is shared, there is always a risk from cross-contamination. The correct calculation of the cleaning validation limits from maximum allowable carryover (MACO) of a marker compound to the next product is vital for the integrity and success of the cleaning validation program. However, the process yielding those limits often involves cumbersome,...
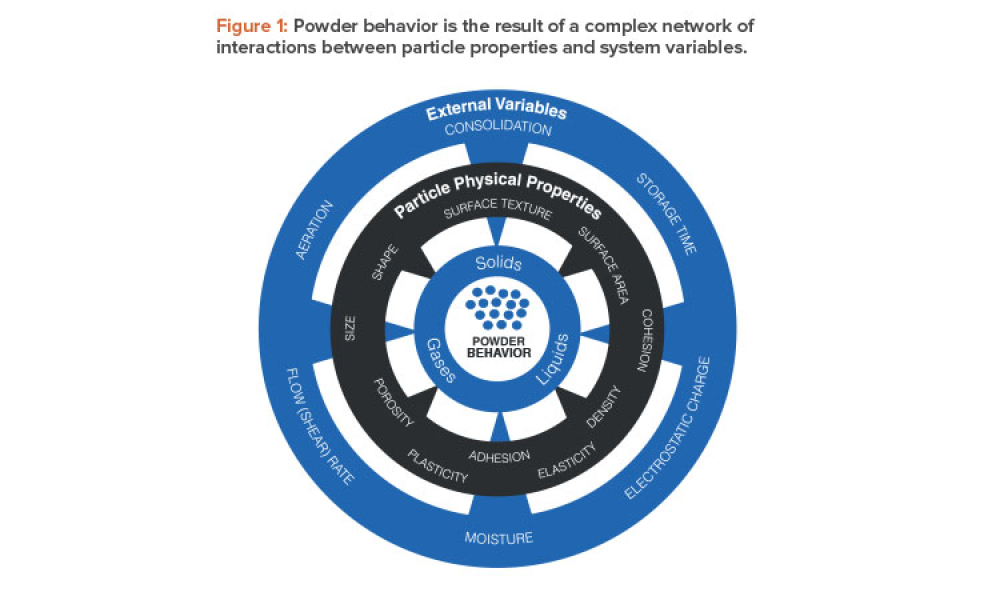
Pharmaceutical manufacturers rely heavily on powder processes, the majority of which are designed and operated on the basis of empirical correlations between material properties and performance. The development of material properties databases for pharmaceutical excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) has the potential to enhance such correlations and, more generally, to...
Industry 4.0 is the recent movement toward intelligent automation technology. In this new era, the integration of modern manufacturing skills and novel information technologies plays an important role on economic competitiveness.1
Robotic process automation (RPA) software automatically handles manual, repetitive, time-consuming, and highly structured tasks such as data entry and back-office functions. Certain processes specific to the pharmaceutical industry represent strong candidates for RPA implementation, with significant potential savings and the possibility of ensuring compliance.