Continuous manufacturing has attracted significant interest over the past decade for small molecules formulated as drug products. The case for adopting continuous manufacturing platforms for manufacturing biologics (i.e., large proteins or biologic products such as vaccines) would, in principle, be even more justified for both quality and business gains. This article briefly reviews continuous...

Downloads
Opportunities in Continuous Manufacturing of Large Molecules
Cover: Continuous manufacturing has attracted significant interest over the past decade for small molecules formulated as drug products. The case for adopting continuous manufacturing platforms for manufacturing biologics (i.e., large proteins or biologic products such as vaccines) would, in principle, be even more justified for both quality and business gains. This article brie y reviews continuous biomanufacturing at a time of very high and global demand for vaccines as well as increased demand for cell and gene therapy products.
Continuous Manufacturing As a Tool for Accelerated Development
Feature: Continuous manufacturing offers one way the pharmaceutical industry can accelerate development of the drug product control strategy to ensure a robust and reliable supply of medicine to the clinic and/or market. This article explores the promise of CM in enhancing accelerated development, as evidenced by experience in solid oral products.
Regulatory Aspects of Global Acceptance of Continuous Manufacturing
Feature: Application of continuous manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry is gaining momentum. Most of the current experience is based on oral solid dosage projects but in the future CM should not be limited to these dosage forms. In this article, the regulatory acceptability of CM to produce pharmaceuticals is demonstrated in different regions, including the “rest of the world” (i.e., regulators in nations and regions other than the US, EU, Japan, and Canada) through case studies.
Software as a Medical Device Fundamentals
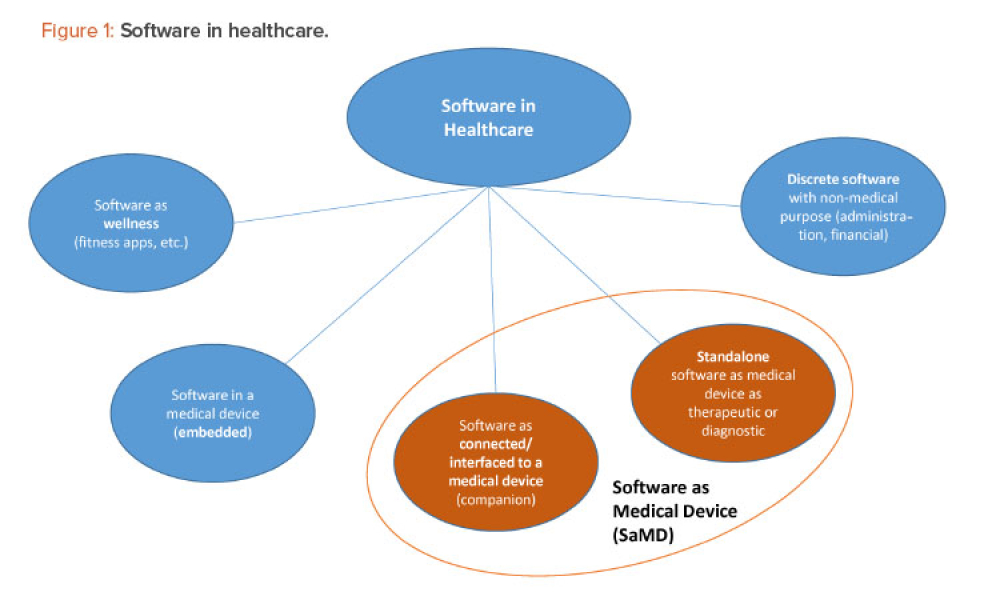
TECHNICAL: Software as a medical device (SaMD) is software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes without being part of a medical device. Although SaMD applications have the potential to improve patient care and expand the pharmaceutical industry’s product lines, companies must understand the distinctive characteristics of this software and address the risks and challenges related to SaMD design, development, regulation, and life-cycle management.
Medical Device UDI Components Management in the European Union
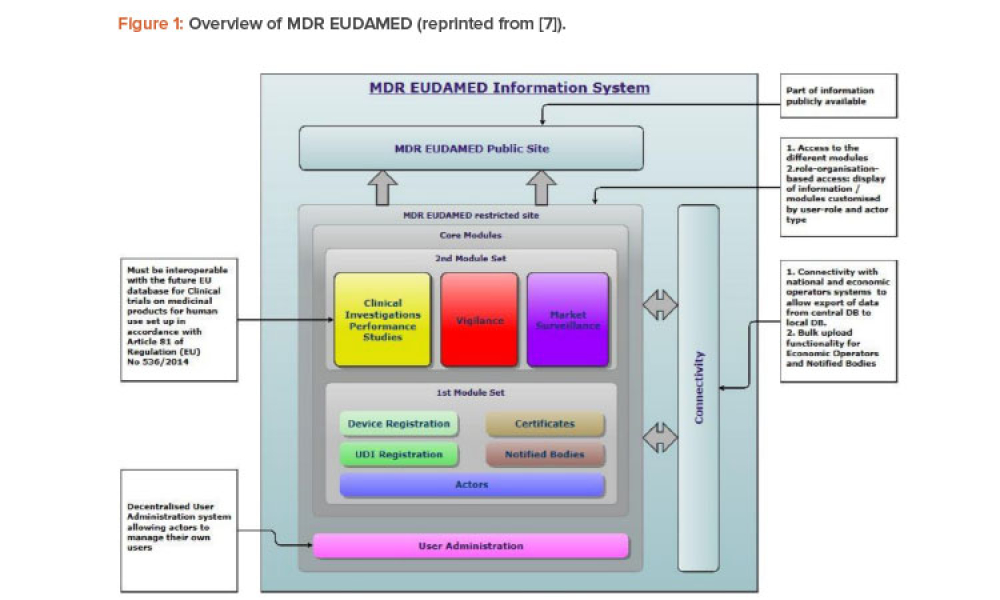
TECHNICAL: Since 2019, the ISPE France Affiliate's Unique Device Identification (UDI) Medical Device Work Group has been producing tools to help project stakeholders within the EU or overseas to understand and comply with EU regulations of UDIs in medical devices. Some of those tools are highlighted in the article.
In This Issue
Organizations wanting to ensure the well-being and growth of their employees need to invest in robust mentorship and recognition programs. Mentoring has played a key role in my career development. In the 1990s and early 2000s, I worked in Novartis and engineering services companies where I was part of informal mentoring groups with some senior directors and trusted collaborators across the...
Remembering the “why” of our pharma industry is so important and, for me, also very personal. My sister Linda was 69 and her four grandchildren were the light of her life. In November 2017, she was diagnosed with appendix cancer (a rare cancer, closely related to colon cancer). After four months of nasty chemotherapy, Linda entered hospice care and died the next month. Previously, my mother...
Optimism is in the air as we move through the summer months and the restrictions that have become second nature are slowly lifting. As I continue the second half of my year as the Emerging Leaders (EL) Chair and representative on...
The pharmaceutical industry in Spain and Portugal is growing, and the ISPE Iberia Affiliate—which has merged the Spain and Portugal Affiliates to take advantage of synergies between the two Affiliates—is working to train and support this expanding market.
The ISPE Foundation Diversity Internship Program has received strong response from applicants and has launched a new partnership.
Software as a medical device (SaMD) is software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes without being part of a medical device.1
Since 2019, the ISPE France Affiliate’s Unique Device Identification (UDI) Medical Device Work Group has been producing tools to help project stakeholders within the EU or overseas understand and comply with EU regulations of UDIs in medical devices. Some of those tools are highlighted in the article.
Powder for oral suspension (PfOS) bioavailability is mostly on the basis of drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. PfOS formulation pH, viscosity, vehicle buffer capacity, drug particle size distribution, density, and viscosity are often critical for absorption. Therefore, careful design and selection of excipients—including suspending agents—are necessary during PfOS formulation...
Continuous manufacturing (CM) offers one way the pharmaceutical industry can accelerate development of the drug product control strategy to ensure a robust and reliable supply of medicine to the clinic and/or market. This article explores the promise of continuous manufacturing in enhancing accelerated development, as evidenced by experience in solid oral products.
Application of continuous manufacturing (CM) in the pharmaceutical industry is gaining momentum. Most of the current experience is based on oral solid dosage (OSD) projects but in the future continuous manufacturing should not be limited to these dosage forms. In this article, the regulatory acceptability of continuous manufacturing to produce pharmaceuticals is demonstrated in different...
The ISPE OSD Community of Practice Continuous Manufacturing Subcommittee is planning a Good Practice Guide to capture information developed over several years by the team to establish equipment requirements, identify opportunities for harmonization and flexible integration, and suggest where current equipment may be enhanced to work with continuous manufacturing platforms of the future.
Cell and gene therapies are complex. As more therapies come to market in the hope of bringing advanced treatments and cures to rare, orphan, and difficult-to-treat diseases, designing quality standards for these personalized medicines is equally as complex.1